Stream
2021, Oct 03
Stream trong Java 8
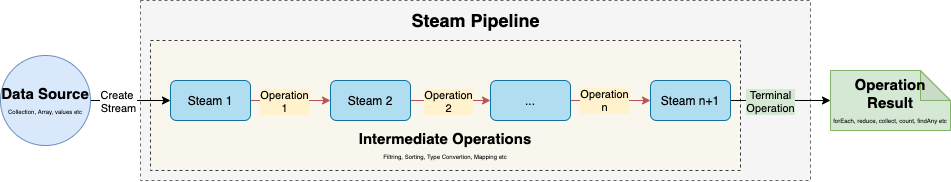
Stream pipeline
Bao gồm
- 1 stream source
- 0 hoặc nhiều intermediate operation
- 1 terminal operation
Intermediate operations
distinct()
- Loại bỏ các phần tử giống nhau
Stream<T> distinct();- Ví dụ:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
numbers.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);Output:
1
2
4
3
7
5
6filter()
- Lọc các phần tử theo điều kiện
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);- Ví dụ: Đếm các String null hoặc empty trong mảng
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("a", "", "b", "c", "ab", "", "ef");
long count = strings.stream()
.filter(string -> string == null || string.isEmpty())
.count();
System.out.println("Number empty: " + count);Output:
Number empty: 2limit()/skip()
- limit lấy các phần tử đầu tiên. skip bỏ các phần tử đầu tiên.
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize);
Stream<T> skip(long n);- Ví dụ: Print 5 phần tử đầu tiên của mảng
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
numbers.stream()
.limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);Output:
1
2
4
3
7map()
- Ánh xạ phần tử sang kết quả khác
<R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);- Ví dụ: Nhân 2 các giá trị trong mảng
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
numbers.stream()
.map(i -> i*2)
.forEach(System.out::println);Output:
2
4
8
6
14
6
10
4
12sorted()
- Sắp xếp các phần tử
Stream<T> sorted();- Ví dụ: Sắp xếp theo thứ tự lớn đến nhỏ
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
numbers.stream()
.sorted((x,y) -> y - x)
.forEach(System.out::println);Output:
7
6
5
4
3
3
2
2
1Terminal Operations
collect()
- Kết hợp thành một Collection
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);- Ví dụ: Tạo một List
List<String> notEmptyList = strings.stream()
.filter(string -> string != null && !string.isEmpty())
.collect(Collectors.toList());forEach()
- Duyệt và thao tác lên từng phần tử
void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action);- Ví dụ: Println từng phần tử trong mảng
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
numbers.stream()
.forEach(System.out::println);Output:
1
2
4
3
7
3
5
2
6anyMatch(), allMatch(), noneMatch()
- anyMatch trả về true nếu có bất kỳ phần tử nào thỏa điều kiện, ngược lại false
- allMatch kiểm tra tất cả phần tử thỏa yêu cầu hay không? noneMatch ngược lại
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);- Ví dụ: Kiểm tra list có chưa số lẻ hay không
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
boolean isContainOdd = numbers.stream()
.anyMatch(x -> x % 2 == 1);min(), max()
- Tìm min, max trong steam
Optional<T> min(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
Optional<T> max(Comparator<? super T> comparator);- Ví dụ: Tìm string dài nhất trong steam
Optional<String> minLength = strings.stream()
.max((x, y) -> (x.length() - y.length()));reduce()
- Kết hợp các phần tử thầnh một giá trị duy nhất
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);- Ví dụ: Tổng các số trong mảng
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4 , 3, 7, 3, 5, 2, 6);
int sum = numbers.stream()
.reduce((x,y) -> x + y).get();
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);Output:
Sum: 33count()
- count đếm số phần tử trong mảng
long count();Source code ở đây