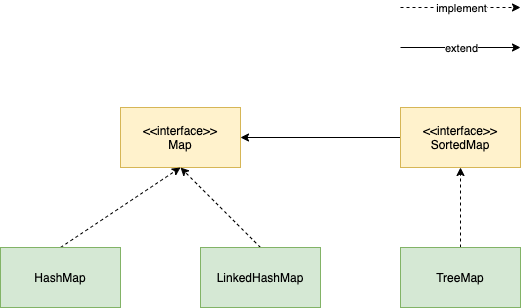
Map
2021, Aug 26
- Khởi tạo và sử dụng HashMap
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "a");
map.put(11111, "a1");
map.put(2, "b");
map.put(2222, "b2");
map.put(3, "c");
map.put(333, "c3");
System.out.println("HashMap");
for (Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Entry <"+ entry.getKey() +"," + entry.getValue() +">");
}Output:
HashMap
Entry <1,a>
Entry <2,b>
Entry <3,c>
Entry <11111,a1>
Entry <333,c3>
Entry <2222,b2>Thứ tự khi duyệt HashMap sẽ tùy thuộc vào giải thuật của nó
- LinkedHashMap sắp xếp các phần tử theo thứ tự insert.
Map<Integer,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put(1, "a");
map.put(11111, "a1");
map.put(2, "b");
map.put(2222, "b2");
map.put(3, "c");
map.put(333, "c3");
System.out.println("LinkedHashMap");
for (Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Entry <"+ entry.getKey() +"," + entry.getValue() +">");
}Output:
Entry <1,a>
Entry <11111,a1>
Entry <2,b>
Entry <2222,b2>
Entry <3,c>
Entry <333,c3>- TreeMap sắp xếp thứ tự các phần tử dựa vào key
Map<Integer,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, "a");
map.put(11111, "a1");
map.put(2, "b");
map.put(2222, "b2");
map.put(3, "c");
map.put(333, "c3");
System.out.println("TreeMap");
for (Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Entry <"+ entry.getKey() +"," + entry.getValue() +">");
}Output:
TreeMap
Entry <1,a>
Entry <2,b>
Entry <3,c>
Entry <333,c3>
Entry <2222,b2>
Entry <11111,a1>Source code ở đây